The top Google algorithm updates of 2021 (chronological)
Google is always rolling out algorithm updates, sometimes announcing them outright and other times in passing—depending on the importance and impact of the update. The biggest update of 2021, of course, is the page experience update, but let’s take a look at what else has changed leading up to that.
1. Passage ranking update (February 2021)
With the passage ranking update, Google can now use artificial intelligence to index not only web pages, but individual passages (paragraphs, sentences) from those pages. This means that specific passages can show up as the featured snippet. The aim is to quickly answer very specific queries, instead of making the user comb through the relevant web page to find it.
Using the example below, Google explains that it can now understand that the passage from the doityourself.com page (B) better answers the query than the wearshade.com result on the (A). “In this case, our systems were able to highlight a featured snippet, but this improvement applies to how we rank web pages overall.
2. "About this result" update (February 2021)
With the ”About this result” of February 2021, Google provides additional context to individual search results so that users can determine which results would be most helpful to them.
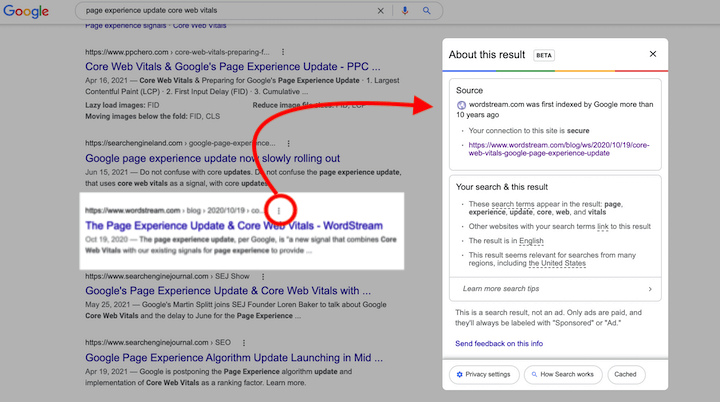
Here’s what the “About this result” box shares:
When the page’s website was first indexed by Google.
Whether your connection to the site is secure.
Which terms that you searched for appear in the page.
Whether other websites with those search terms link to the page.
The language of the page.
Whether it seems relevant for this search in many regions.
And if you have a Wikipedia reference, it will pull a brief description from there (not meta tags this time).
By learning about a source before opening the results, a user can determine if the site is trustworthy or not. This would particularly aid user discovery of authoritative and trustworthy but unpopular websites. However, the feature remains in beta mode.
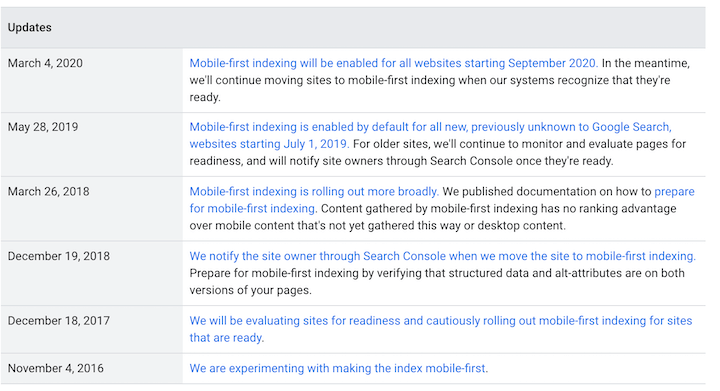
3. 100% mobile-first indexing update (March 2021)
With the rise of mobile traffic in the 2010s, Google began placing more importance on mobile friendliness as a ranking factor in 2015. A year later, mobile-first indexing was introduced — which refers to when Google crawls—and therefore ranks—your website pages according to the mobile version of that content.Image source
As of July 2019, mobile-first indexing became the default for all new websites. And as of June 2021, it became the default for all websites, old and new.
To optimize for mobile friendliness:
Make sure you have a responsive site.
Use lazy loading and image compression.
Always manually test popups and form functionalities on your mobile phone
Mobile-friendliness works on a page-by-page basis, but you can find site-wide mobile performance measurements with the mobile usability report in Search Console and Google's Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
4. Product reviews update (April 2021)
The goal of Google’s April 2021 product reviews update was to encourage product reviews that don't just summarize a list of products, but rather provide in-depth research, insightful analysis, and original content. So to create product review content that’s of high quality, Google recommends that you:
Express expert knowledge of the products.
Share unique content beyond what the manufacturer provides.
Provide quantitative measurements for performance.
Compare it to previous models and other products.
Help consumers make a wise purchasing decision.
This review of Wix by Website Tool Tester is an example of such an in-depth product review. It’s 3,500 words of content that feature a detailed comparison of competing products, an interactive plan finder, FAQs, an actively managed comments section, screenshots, and even videos.
5. MUM update (May 2021)
Google has been making strides with AI in its algorithms, the most recent being the May 2021 MUM update.
Multitask Unified Model (MUM) is a natural language model that is significantly more powerful than BERT of October 2019 (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers).
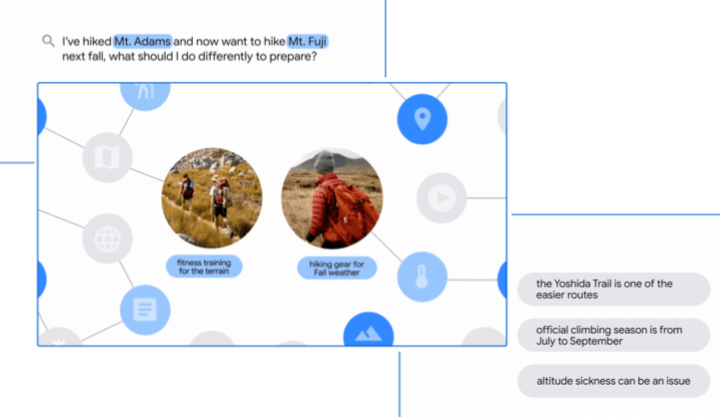
MUM is designed for “Helping you when there isn’t a simple answer.” The goal of MUM is to use contextual information from different sources to present comprehensive answers to complex questions.
So instead of having to search:
"How to prepare to hike mount adams," and then
"How to prepare to hike mount fuji," and then
"Mount adams vs mount fuji hiking,"
a person can ask
“I've hiked Mt. Adams and now want to hike Mt. Fuji next fall, what should I do differently to prepare?”
and learn it all in one search.
MUM is being trained across 75 languages, so it can identify relevant answers in languages other than the one in which the query was written.
This doesn't mean you should start writing posts that anaswer complex questions. Just be sure to do your keyword research and keep publishing long-form content that targets long-tail and question keywords.
It had two phases, which Google said would each start and finish on the same day—but it actually took two weeks longer than expected. There weren't many details
on this update, but it’s always good to check and make sure your website is protected from spam.
You should be especially careful of these malicious actors if your website provides user interaction via comments, forums, etc. Here are some tips to protect your website from spammers:
- Update your website’s SSL certificate
- Use Google Search Console to check for security issues and manual action reports.
- Do regular clean-ups of suspected spammy actions such as multiple requests from an IP address.
- Use noindex to prevent Google from indexing low-trust pages, especially the ones that display user-generated content. Alternatively, you can mark the links as nofollow.
In addition to indexing the mobile version of websites, Google has also introduced a specific set of metrics through the page experience update called Core Web Vitals.
These are not new metrics, but rather newly prioritized factors to quantify a person’s experience of a webpage.
These include:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): how fast the main content of a page loads.
First Input Delay (FID): how quickly a webpage responds to the user’s first action on the page.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): how stable the layout is (i.e., elements don't jump around unexpectedly).
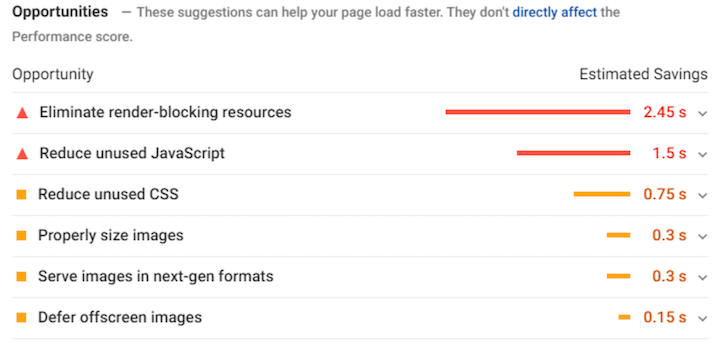
- Eliminate intrusive interstitials or banners that block content.
- Reduce Javascript execution
- Implement lazy loading
- Optimize and compress images
- Provide proper dimensions for images and embeds
- Improve server response time
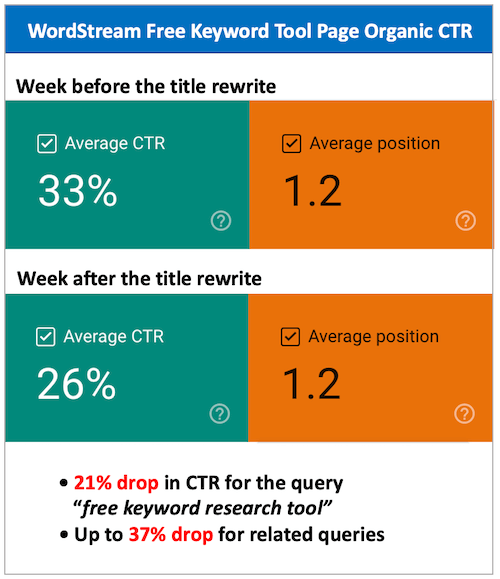
For over a decade, Google has been tweaking page titles in the SERP according to the query. But starting on August 16, people began noticing that Google was drastically changing their page titles, often in a detrimental way. A week later, Google confirmed that it introduced a new system that will no longer adjust titles according to queries, but to better represent the page as a whole.
This update is not being received well, since titles are being generated from H1s, image tags, and even anchor text from other pages. As of the date of writing this post, the story is still unfolding, but you can learn more about the page title update here.
The page title update has negatively impacted many sites, including ours!
Google algorithm updates of 2021 [recap]
SEO is a comprehensive and progressive strategy, and updates shouldn't impact your rankings too much as long as you stay focused on EAT and best practices. But as a marketer, webmaster, or business owner, it's important to monitor updates and report on your performance so you can refine your strategy and leverage existing opportunities. The updates we covered in this post are:
- Passage ranking
- About this result
- Product reviews
- MUM
- Link spam
- Mobile-first indexing
- Page experience
- Page titles

No comments:
Post a Comment